Heart
The center of the circulatory system is the heart, which is the main pumping mechanism. The heart is made of muscle. The heart is shaped something like a cone, with a pointed bottom and a round top. It is hollow so that it can fill up with blood. An adult’s heart is about the size of a large orange and weighs a little less than a pound.
The heart is in the middle of the chest. It fits snugly between the two lungs. It is held in place by the blood vessels that carry the blood to and from its chambers. The heart is tipped somewhat so that there is a little more of it on the left side than on the right. The pointed tip at the bottom of the heart touches the front wall of the chest. Every time the heart beats it goes “thump” against the chest wall. You can feel the thumps if you press there with your hand. You can also listen to them with your ear.
Blood (blud) the fluid circulating through the heart, arteries, capillaries, and veins, carrying
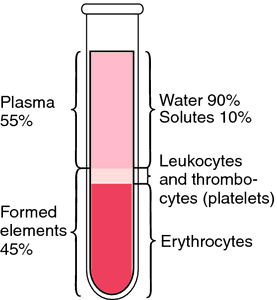
nutriment and oxygen to body cells, and removing waste products and carbon dioxide. It consists of the liquid portion (the plasma) and the formed elements (erythrocytes, leukocytes, and platelets).
arterial blood oxygenated blood, found in the pulmonary veins, the left chambers of the heart, and the systemic arteries.
citrated blood blood treated with sodium citrate or citric acid to prevent its coagulation.
cord blood that contained in umbilical vessels at time of delivery of the infant.
occult blood that present in such small quantities that it is detectible only by chemical tests or by spectroscopic or microscopic examination.
predonated autologous blood blood donated prior to surgery or other invasive procedure for use in a possible autotransfusion.
venous blood blood that has given up its oxygen to the tissues and is carrying carbon dioxide back through the systemic veins for gas exchange in the lungs.
whole blood that from which none of the elements has been removed, sometimes specifically that drawn from a selected donor under aseptic conditions, containing citrate ion or heparin, and used as a blood replenisher.
Circulatory System : The circulatory system is an organ system that permits blood and lymph circulation to transport nutrients (such as amino acids and electrolytes), oxygen, carbon dioxide, hormones, blood cells, etc. to and from cells in the body to nourish it and help to fight diseases, stabilize body temperature and pH, and to maintain homeostasis.
Blood, Heart and Circulation Topics
The center of the circulatory system is the heart, which is the main pumping mechanism. The heart is made of muscle. The heart is shaped something like a cone, with a pointed bottom and a round top. It is hollow so that it can fill up with blood. An adult’s heart is about the size of a large orange and weighs a little less than a pound.
The heart is in the middle of the chest. It fits snugly between the two lungs. It is held in place by the blood vessels that carry the blood to and from its chambers. The heart is tipped somewhat so that there is a little more of it on the left side than on the right. The pointed tip at the bottom of the heart touches the front wall of the chest. Every time the heart beats it goes “thump” against the chest wall. You can feel the thumps if you press there with your hand. You can also listen to them with your ear.
Blood (blud) the fluid circulating through the heart, arteries, capillaries, and veins, carrying
nutriment and oxygen to body cells, and removing waste products and carbon dioxide. It consists of the liquid portion (the plasma) and the formed elements (erythrocytes, leukocytes, and platelets).
arterial blood oxygenated blood, found in the pulmonary veins, the left chambers of the heart, and the systemic arteries.
citrated blood blood treated with sodium citrate or citric acid to prevent its coagulation.
cord blood that contained in umbilical vessels at time of delivery of the infant.
occult blood that present in such small quantities that it is detectible only by chemical tests or by spectroscopic or microscopic examination.
predonated autologous blood blood donated prior to surgery or other invasive procedure for use in a possible autotransfusion.
venous blood blood that has given up its oxygen to the tissues and is carrying carbon dioxide back through the systemic veins for gas exchange in the lungs.
whole blood that from which none of the elements has been removed, sometimes specifically that drawn from a selected donor under aseptic conditions, containing citrate ion or heparin, and used as a blood replenisher.
Circulatory System : The circulatory system is an organ system that permits blood and lymph circulation to transport nutrients (such as amino acids and electrolytes), oxygen, carbon dioxide, hormones, blood cells, etc. to and from cells in the body to nourish it and help to fight diseases, stabilize body temperature and pH, and to maintain homeostasis.
Blood, Heart and Circulation Topics
- Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm see Aortic Aneurysm
- ABO Blood Groups see Blood
- Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia see Acute Lymphocytic Leukemia
- Acute Lymphocytic Leukemia
- Acute Myeloblastic Leukemia see Acute Myeloid Leukemia
- Acute Myeloid Leukemia
- AF see Atrial Fibrillation
- ALL see Acute Lymphocytic Leukemia
- AML see Acute Myeloid Leukemia
- Anatomy
- Anemia
- Aneurysms
- Angiitis see Vasculitis
- Angina
- Angioplasty
- Anticoagulants see Blood Thinners
- Antihypertensive Medicines see Blood Pressure Medicines
- Anti-platelet drugs see Blood Thinners
- Aortic Aneurysm
- Aortic Dissection see Aortic Aneurysm
- Aortic Stenosis see Heart Valve Diseases
- Aplastic Anemia
- Arrhythmia
- Arteriosclerosis see Atherosclerosis
- Arteriosclerosis, Coronary see Coronary Artery Disease
- Arteriosclerosis of Extremities see Peripheral Arterial Disease
- Arteriovenous Malformations
- Atherosclerosis
- Atherosclerosis, Coronary see Coronary Artery Disease
- Atrial Fibrillation
- Automated External Defibrillators see Cardiac Arrest
- AVM see Arteriovenous Malformations
- Behcet's Syndrome
- Berry Aneurysm see Brain Aneurysm
- Bleeding
- Bleeding Disorders
- Blood
- Blood Cells see Blood
- Blood Clots
- Blood Coagulation Disorders see Bleeding Disorders; Hemophilia
- Blood Disorders
- Blood Donation see Blood Transfusion and Donation
- Blood Platelet Disorders see Platelet Disorders
- Blood Pressure see High Blood Pressure; Low Blood Pressure
- Blood Pressure Medicines
- Blood Thinners
- Blood Transfusion and Donation
- Bradycardia see Arrhythmia
- Brain Aneurysm
- Brain Attack see Stroke
- Bypass Surgery see Coronary Artery Bypass Surgery
- CABG see Coronary Artery Bypass Surgery
- CAD see Coronary Artery Disease
- Cardiac Arrest
- Cardiac Diseases see Heart Diseases
- Cardiac Failure see Heart Failure
- Cardiac Rehabilitation
- Cardiac Surgery see Heart Surgery
- Cardiomyopathy
- Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation see CPR
- Cardiovascular Diseases see Heart Diseases; Vascular Diseases
- Carotid Artery Disease
- Carotid Endarterectomy see Carotid Artery Disease; Stroke
- Cerebral Aneurysm see Brain Aneurysm
- Cerebrovascular Disease see Stroke
- Chest Pain
- CHF see Heart Failure
- Childhood Leukemia
- Cholesterol
- Chronic Granulocytic Leukemia see Chronic Myeloid Leukemia
- Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia
- Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia see Chronic Myeloid Leukemia
- Chronic Myeloid Leukemia
- Churg-Strauss Syndrome see Eosinophilic Disorders
- Circulatory Disorders see Vascular Diseases
- Claudication see Peripheral Arterial Disease
- CLL see Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia
- CML see Chronic Myeloid Leukemia
- Congenital Heart Defects
- Congestive Heart Failure see Heart Failure
- Cooley's Anemia see Thalassemia
- Cor Pulmonale see Pulmonary Hypertension
- Coronary Arteriosclerosis see Coronary Artery Disease
- Coronary Artery Bypass Graft see Coronary Artery Bypass Surgery
- Coronary Artery Bypass Surgery
- Coronary Artery Disease
- CPR
- CVA see Stroke
- Deep Vein Thrombosis
- Defibrillators, Implantable see Pacemakers and Implantable Defibrillators
- Diabetic Foot
- Diabetic Heart Disease
- Dropsy see Edema
- DVT see Deep Vein Thrombosis
- Edema
- Endocarditis
- Eosinophilia see Eosinophilic Disorders
- Eosinophilic Disorders
- Erythroblastosis Fetalis see Rh Incompatibility
- Familial Combined Hyperlipidemia see Cholesterol; Triglycerides
- Familial Dysbetalipoproteinemia see Cholesterol
- Familial Hypercholesterolemia see Cholesterol
- Familial Hypertriglyceridemia see Triglycerides
- Fanconi Anemia see Aplastic Anemia
- Gangrene
- Gas Gangrene see Gangrene
- Giant Cell Arteritis
- Granulomatosis with Polyangiitis (Wegener's)
- Hairy Cell Leukemia see Leukemia
- Hardening of the Arteries see Atherosclerosis
- HDL see Cholesterol
- Heart Attack
- Heart Defects see Congenital Heart Defects
- Heart Disease in Women
- Heart Diseases
- Heart Diseases, Congenital see Congenital Heart Defects
- Heart Diseases--Prevention
- Heart Diseases--Rehabilitation see Cardiac Rehabilitation
- Heart Failure
- Heart Murmur see Congenital Heart Defects; Heart Valve Diseases
- Heart Surgery
- Heart Transplantation
- Heart Valve Diseases
- Hemangioma see Vascular Diseases
- Hematologic Disorders see Blood Disorders
- Hematoma see Bleeding
- Hemoglobin SS Disease see Sickle Cell Anemia
- Hemolytic Disease of Newborn see Rh Incompatibility
- Hemophilia
- Hemorrhage see Bleeding
- High Blood Pressure
- High Blood Pressure Medicines see Blood Pressure Medicines
- Hypercholesterolemia see Cholesterol
- Hypereosinophilic Syndrome see Eosinophilic Disorders
- Hyperlipidemia see Cholesterol; Triglycerides
- Hypertension see High Blood Pressure
- Hypertension, Pulmonary see Pulmonary Hypertension
- Hypertriglyceridemia see Triglycerides
- Hypotension see Low Blood Pressure
- Implantable Defibrillators see Pacemakers and Implantable Defibrillators
- Insulin Resistance see Metabolic Syndrome
- Intermittent Claudication see Peripheral Arterial Disease
- Intracranial Aneurysm see Brain Aneurysm
- Iron Deficiency Anemia see Anemia
- Irregular Heartbeat see Arrhythmia
- Kawasaki Disease
- LDL see Cholesterol
- Leukemia
- Leukemia, Acute Lymphoblastic see Acute Lymphocytic Leukemia
- Leukemia, Acute Lymphocytic see Acute Lymphocytic Leukemia
- Leukemia, Childhood see Childhood Leukemia
- Leukemia, Chronic Lymphocytic see Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia
- Leukemia, Myeloblastic, Acute see Acute Myeloid Leukemia
- Leukemia, Myelogenous, Acute see Acute Myeloid Leukemia
- Leukemia, Myeloid, Acute see Acute Myeloid Leukemia
- Leukemia, Myeloid, Chronic see Chronic Myeloid Leukemia
- Low Blood Pressure
- Lymphatic Obstruction see Lymphedema
- Lymphedema
- Malaria
- Mediterranean Anemia see Thalassemia
- Metabolic Syndrome
- MI see Heart Attack
- Mini-Stroke see Transient Ischemic Attack
- Mitral Valve Prolapse
- Mucocutaneous Lymph Node Syndrome see Kawasaki Disease
- Multifocal Atrial Tachycardia see Arrhythmia
- Myocardial Infarction see Heart Attack
- Open Heart Surgery see Heart Surgery
- Orthostatic Hypotension see Low Blood Pressure
- Pacemakers and Implantable Defibrillators
- PAD see Peripheral Arterial Disease
- Pain, Chest see Chest Pain
- Pericardial Disorders
- Pericardial Effusion see Pericardial Disorders
- Pericarditis see Pericardial Disorders
- Peripheral Arterial Disease
- Plaque, Atherosclerotic see Atherosclerosis
- Platelet Disorders
- Primary Pulmonary Hypertension see Pulmonary Hypertension
- Pulmonary Hypertension
- Raynaud's Disease
- Rh Incompatibility
- SCA see Cardiac Arrest
- Septic Shock see Shock
- Shock
- Shy-Drager Syndrome see Low Blood Pressure
- Sickle Cell Anemia
- Sickle Cell Disease see Sickle Cell Anemia
- Spider Veins see Varicose Veins
- Stroke
- Sudden Cardiac Death see Cardiac Arrest
- Syndrome X (Cardiac) see Angina
- Syndrome X (Metabolic) see Metabolic Syndrome
- Tachycardia see Arrhythmia
- Temporal Arteritis see Giant Cell Arteritis
- Thalassemia
- Thoracic Aortic Aneurysm see Aortic Aneurysm
- Thrombocytopenia see Platelet Disorders
- Thrombophlebitis see Blood Clots
- TIA see Transient Ischemic Attack
- Transfusion see Blood Transfusion and Donation
- Transient Ischemic Attack
- Triglycerides
- Valvular Heart Diseases see Heart Valve Diseases
- Varicose Veins
- Vascular Diseases
- Vasculitis
- Veins see Varicose Veins; Vascular Diseases
- Venous Thrombosis see Blood Clots; Deep Vein Thrombosis
- von Willebrand's Disease see Platelet Disorders
- Wegener's Granulomatosis see Granulomatosis with Polyangiitis (Wegener's)

No comments:
Post a Comment